Introduction:
-
- Carbon, the versatile building block of life, plays a critical role in regulating Earth’s climate. Its constant movement through various reservoirs, known as the carbon cycle, maintains a delicate balance. As environmental experts, understanding the carbon cycle and its response to human activities is crucial for addressing climate change.
The Carbon Cycle’s Symphony:
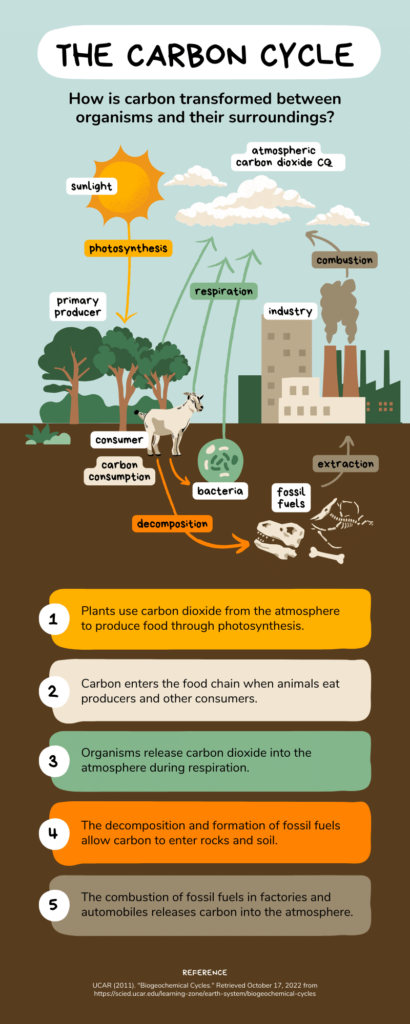
The carbon cycle is a complex yet elegant dance between the atmosphere, biosphere, geosphere, and hydrosphere. Here’s a breakdown of the key players:
-
- Atmosphere: Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the main reservoir of carbon in the atmosphere. Plants utilize CO2 during photosynthesis, while natural processes like respiration release it back.
-
- Biosphere: Living organisms, from towering trees to microscopic plankton, store carbon through photosynthesis. Dead organic matter decomposes, returning carbon to the atmosphere or getting buried underground.
-
- Geosphere: Fossil fuels like coal and oil represent vast stores of ancient carbon sequestered over millennia. Geological processes like weathering and volcanic eruptions also influence carbon movement.
-
- Hydrosphere: The oceans absorb a significant amount of atmospheric CO2, playing a vital role in regulating atmospheric carbon levels.
Human Interference and the Disrupted Rhythm:
Human activities like burning fossil fuels for energy and deforestation significantly disrupt the carbon cycle. The excessive release of CO2 disrupts the natural balance, leading to:
-
- Increased Atmospheric CO2: Burning fossil fuels in power plants and vehicles releases large quantities of CO2, exceeding the natural capacity of the biosphere and oceans to absorb it.
-
- Ocean Acidification: As oceans absorb more atmospheric CO2, they become more acidic, harming marine ecosystems.
-
- Global Warming: Increased greenhouse gas concentration traps heat, leading to rising global temperatures and associated climate change impacts, like extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
The Urgency of Restoring Balance:
Climate change necessitates immediate action to restore the carbon cycle’s balance. Here are some approaches:
-
- Renewable Energy Transition: Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can drastically reduce CO2 emissions.
- Sustainable Forestry Practices: Protecting existing forests and promoting reforestation enhances carbon sequestration by natural ecosystems.
- Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies: Research and development in capturing CO2 emissions from power plants and storing them underground can be a game-changer.
- Individual Responsibility: Adopting energy-efficient practices and reducing our carbon footprint through conscious consumption can collectively contribute to a positive impact.
Conclusion:
-
- The carbon cycle is the foundation of a healthy planet. As environmental experts, we have a responsibility to educate the public and policymakers about its significance. By implementing sustainable practices and embracing innovative solutions, we can ensure the carbon cycle continues its vital dance, maintaining a healthy planet for generations to come. Let’s work together to restore balance and ensure a harmonious future for all.
Mains Questions:

Question 1:
The carbon cycle is a critical natural process for regulating Earth’s climate. Explain the various components of the carbon cycle and how human activities are disrupting its delicate balance. Discuss the potential consequences of this disruption. (250 words)
Model Answer:
Components of the Carbon Cycle:
-
- Atmosphere: Contains CO2, the main greenhouse gas, vital for plant life but contributing to global warming at high levels.
- Biosphere: Living organisms like plants absorb CO2 for photosynthesis and release it through respiration. Dead organic matter decomposes, returning carbon to the atmosphere or getting buried underground.
- Geosphere: Fossil fuels like coal and oil represent vast stores of ancient carbon. Geological processes also influence carbon movement.
- Hydrosphere: Oceans absorb a significant amount of atmospheric CO2, playing a crucial role in regulating its levels.
Human Disruption of the Carbon Cycle:
-
- Fossil Fuel Burning: Burning fossil fuels releases large quantities of CO2 exceeding the natural absorption capacity of the biosphere and oceans.
- Deforestation: Reduces the carbon sink capacity of forests, leading to more CO2 in the atmosphere.
- Land-use Change: Conversion of forests to agriculture releases stored carbon.
Consequences of Disruption:
-
- Global Warming: Increased CO2 traps heat, leading to rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and rising sea levels.
- Ocean Acidification: Oceans absorbing more CO2 become more acidic, harming marine ecosystems.
- Disruptions in Ecosystems: Climate change disrupts natural habitats and ecological processes.
Question 2:
As an environmental expert, propose strategies to mitigate the disruption of the carbon cycle caused by human activities. Discuss the role of individual responsibility and government policies in achieving a sustainable carbon cycle. (250 words)
Model Answer:
Mitigation Strategies:
-
- Transition to Renewable Energy: Shifting from fossil fuels to solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources can drastically reduce CO2 emissions.
- Sustainable Forest Management: Protecting existing forests and promoting reforestation enhances carbon sequestration by natural ecosystems.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Research and development in capturing CO2 emissions from power plants and storing them underground can be a game-changer.
- Energy Efficiency: Promoting energy-efficient practices and technologies minimizes overall energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
Individual Responsibility and Government Policies:
-
- Individuals: Adopting energy-efficient practices at home and work, reducing carbon footprint through conscious consumption, and supporting sustainable businesses can contribute collectively.
- Government Policies: Implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, promoting renewable energy through subsidies and incentives, and investing in green infrastructure are crucial measures.
Conclusion:
-
- Restoring balance to the carbon cycle requires a multi-pronged approach. Individual responsibility coupled with strong government policies and technological advancements can ensure a sustainable future for all.
Attempt Quiz based on above!
Read in Hindi
Remember: These are just sample answers. It’s important to further research and refine your responses based on your own understanding and perspective. Read entire UPSC Current Affairs.
Relevance to the UPSC Prelims and Mains syllabus under the following topics:

Prelims:
-
- General Science: This section might indirectly touch upon concepts related to biogeochemical cycles and their importance in maintaining ecological balance. You could mention the carbon cycle as an example while answering a question about biogeochemical cycles.
Mains:
-
- Essay: Topics related to environmental sustainability, climate change, or the impact of human activities on the environment could provide an opportunity to discuss the carbon cycle and its disruption.
- General Studies III (Technology, Economic Development, Security and Social Development): This section is most relevant for discussing the human impact on the carbon cycle through activities like industrialization, energy consumption, and deforestation. You can also mention mitigation strategies like renewable energy and sustainable development.
- Optional Subjects (if applicable): Some optional subjects like Geography, Environment and Ecology, or Science and Technology might have a more specific focus on the carbon cycle and its role in the environment.









0 Comments